Finding distance on a 2D grid again: how many steps it takes to move from (1,1) to (31,39) if some paths are blocked by walls?
Finding empty spaces
We need to determine if a given point is a wall or an empty space by doing a simple calculation and then checking bit parity. First, let's define the data structure for the grid points and create the function that check if the space is empty. Python 3.10 has a handy function bit_count.
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Point:
x: int
y: int
def is_empty(point: Point) -> bool:
v = point.x**2 + 3*point.x + 2*point.x*point.y + point.y + point.y**2 + FAVNUM
return v.bit_count() %2==0
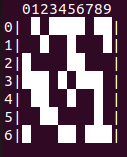
Let's check with the sample data:
print(" 0123456789")
for y in range(7):
print(y,end="|")
for x in range(10):
if is_empty(Point(x,y)):
print(" ", end="")
else:
print("█", end="")
print("|")
Breadth First Search
A classic BFS algorithm should work. We need a queue of points to check, we need to record the points already checked and we need a starting point. Here it goes:
start_point=Point(1,1)
visited=set()
to_check=deque()
to_check.append(start_point)
visited.add(start_point)
We then iterate over the queue until it's empty or we find the solution. Pop the point to check
and then get the neighbours: for p in get_next_points(current_point):. Now we just have to write the
get_next_points function.
Getting next points
We can move left, right, up or down from the current point - that's -1 or +1. We can't go diagonaly and also we don't want to return the current point. So, x can be -1 or 1 while y is 0, or vice versa. The easiest way to write it is:
for deltax in [-1, 0, 1]:
for deltay in [-1, 0, 1]:
if abs(deltax)==abs(deltay):
continue
The instruction says: "The cube maze starts at 0,0 and seems to extend infinitely toward positive x and y".
But I added a sanity check. If either x or y gets too large, I skip the point, just like I skip the negatives.
We also need to skip walls: if not is_empty(newpoint): continue
Recording distance
- starting point has a distance of 0 from the starting point (obviously)
- all other points are initialized with infinity (in practice, a value much larger then expected will do)
- new point gets a distance 1 larger then the previous point, but here's an important thing: only if it's smaller then the previously recorded distance (we can get to a point more than once and we're only interested in the shortest path)
I used a dict of Points to keep distances and wrapped them in a class for convenience. I later added a function that prints the map.
class Map:
distance: dict={}
def __init__(self):
for x in range(MAXX):
for y in range(MAXY):
self.distance[Point(x, y)] = MAXDISTANCE
self.distance[Point(1,1)]=0
We need some answers
For part 1, we need to reach a specific point. Then we can stop the calculations:
if p==target: return floormap.distance[p]
For part 2, we need to know how many points can be reached in 50 steps or less.
Since we recorded all the distances, we can just find them in one line using
dict comprehension: sum(v <= 50 for v in floormap.distance.values())
Code
#!/usr/bin/python3
from dataclasses import dataclass
from collections import deque
from os import get_terminal_size
FAVNUM=1350
#FAVNUM=10
MAXX=MAXY=200
MAXDISTANCE=9999
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Point:
x: int
y: int
class Map:
distance: dict={}
def __init__(self):
for x in range(MAXX):
for y in range(MAXY):
self.distance[Point(x, y)] = MAXDISTANCE
self.distance[Point(1,1)]=0
def print(self):
width = min(get_terminal_size()[0]//3,MAXX)
height = min(get_terminal_size()[1]-3,MAXX)
for y in range(height):
for x in range(width):
p=Point(x,y)
if is_empty(p):
d=self.distance[p]
if d<MAXDISTANCE:
print(f"{d:02d}", end=" ")
else:
print(" ", end="")
else:
print("███", end="")
print("")
def is_empty(point: Point) -> bool:
v = point.x**2 + 3*point.x + 2*point.x*point.y + point.y + point.y**2 + FAVNUM
return v.bit_count() %2==0
def get_next_points(p: Point) -> Point:
global floormap
for deltax in [-1, 0, 1]:
for deltay in [-1, 0, 1]:
if abs(deltax)==abs(deltay): # don't go diagonal
continue
newx=p.x+deltax
newy=p.y+deltay
if newx<0 or newy<0 or newx>=MAXX or newy>=MAXY:
continue
newpoint=Point(newx, newy)
if not is_empty(newpoint):
continue
newdistance=floormap.distance[p]+1
floormap.distance[newpoint]=min(floormap.distance[newpoint],newdistance)
yield newpoint
def calculate_distances(target: Point) -> int:
global floormap
start_point=Point(1,1)
visited=set()
to_check=deque()
to_check.append(start_point)
visited.add(start_point)
while to_check:
current_point=to_check.popleft()
for p in get_next_points(current_point):
if p in visited:
continue
if p==target:
return floormap.distance[p]
to_check.append(p)
visited.add(p)
floormap=Map()
part1answer=calculate_distances(Point(31,39))
print(f"Part 1: {part1answer}")
part2answer = sum(v <= 50 for v in floormap.distance.values())
print(f"Part 2: {part2answer}")
#floormap.print()